Mold Making - The Unsung Metal Artisans Behind Countless Products
1. Introduction to mold making service
1.1. What is mold making service?
Mold making service is the process of designing, fabricating, and testing molds for mass production of products. Molds are often referred to as the “frameworks” that define the shape of a product. They play a crucial role in forming, positioning, and ensuring the accuracy of the product. While molds may appear to be simple metal tools, they possess extraordinary power in shaping products. Each mold is meticulously crafted to fulfill the mission of producing a vast quantity of identical, high-quality products down to the finest detail.
1.2. Mold components
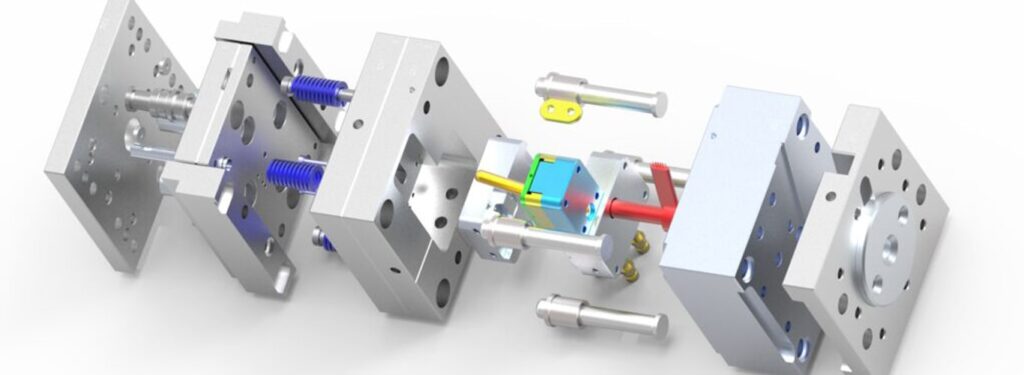
The composition of molds can vary depending on the type of mold, the complexity of the product, and the production requirements. However, most types of molds generally include the following main components:
Frame system
- Fixed Platen: The main component of the mold, it withstands the pressing force and keeps the other mold components fixed during production.
- Moving Platen: Can move in a specific direction to create the material cavity and remove the product from the mold.
- Guide Rails: Help the moving platen move accurately and smoothly during production.
- Guide Bushings: Reduce friction and support the movement of the moving platen.
Forming system
- Core: Creates the inner shape of the product. The core can be made of steel, aluminum, copper, plastic, or other materials depending on the requirements.
- Cavity: Creates the outer shape of the product. The cavity can be made of steel, aluminum, copper, plastic, or other materials depending on the requirements.
- Ejector: Helps position and support the core and cavity during production.
- Ejector Pins: Help push the product out of the mold after production.
Material delivery system
- Runners: Convey material from the delivery system to the material cavity in the mold.
- Sprue: The point at which material is injected into the material cavity.
- Flow control valve: Controls the flow of material into the material cavity.
Cooling system
- Cooling channels: Circulate water or coolant through the mold components to dissipate heat.
- Temperature control unit: Controls the mold temperature during production.
Lubrication system
- Guide bushings: Reduce friction between moving mold components.
- Oil pump system: Supplies lubricant to the guide bushings.
Safety system
- Safety sensors: Detect malfunctions during production and automatically shut down the system for safety.
- Safety doors: Prevent operators from accessing hazardous mold components during production.
- In addition, some molds may also include other components such as a venting system, a vacuum system, a pressure control system, etc.

2. Mold making process
2.1. Mold design
- Product, quantity, material, manufacturing method, accuracy, and other requirements analysis: Conduct a thorough analysis of the product’s specifications, including its intended use, production volume, material selection, manufacturing method, required accuracy, and other relevant factors.
- 3D design using specialized software: Utilize computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software to create a detailed 3D model of the mold. This model should accurately represent the mold’s components, dimensions, and tolerances.
- Detailed engineering drawings for each mold component: Generate detailed engineering drawings for each component of the mold, specifying dimensions, tolerances, material specifications, heat treatment requirements, and other pertinent information.
- Simulation analysis: Employ simulation software to analyze stress distribution, flow patterns, temperature distribution, and other critical parameters during the mold’s operation. This analysis helps identify potential issues and optimize the mold design.
2.2. Mold making
- Material selection: Carefully select appropriate mold materials based on the required strength, heat resistance, wear resistance, and other performance criteria.
- Rough machining: Employ rough machining techniques such as cutting, milling, turning, and grinding to establish the basic form of the mold components.
- Precision machining: Utilize precision machining methods like electrical discharge machining (EDM) and computer numerical control (CNC) machining to achieve the high dimensional accuracy and surface finish required for mold components.
- Heat treatment: Subject the mold components to appropriate heat treatment processes to enhance their hardness, durability, and wear resistance.
2.3. Mold assembly and testing
- Mold assembly: Assemble the mold components according to the detailed engineering drawings, ensuring proper alignment, fit, and functionality.
- Accuracy and dimensional inspection: Conduct rigorous inspections to verify the accuracy, dimensions, and tolerances of individual components and the overall mold assembly.
- Mold testing: Perform mold testing by producing a small batch of trial products. Evaluate the product quality, identify any defects, and assess the mold’s performance.
- Mold adjustment: Make necessary adjustments to the mold based on the results of the testing phase to ensure product quality meets the specified requirements.
2.4. Finalization and delivery
- Finalization: Thoroughly clean, lubricate, and preserve the mold to prevent corrosion and maintain its condition.
- Delivery and documentation: Deliver the mold to the customer along with comprehensive user manuals and maintenance guidelines.



3. Applications of mold making services
Molds play a pivotal role in various industries, serving as the silent metalworkers that shape a vast array of diverse and high-quality products. Their significance extends far beyond the realm of manufacturing, shaping our daily lives and influencing countless aspects of modern society.
3.1. Mold manufacturing in diverse industries
- Plastics manufacturing: Production of food packaging, children’s toys, phone cases, automotive components, and an extensive range of plastic products.
- Automotive component manufacturing: Fabrication of front bumpers, headlights, car interior components, and other essential automotive parts.
- Electronics industry: Manufacturing of computer cases, mobile phone housings, electronic components, and various electronic devices.
- Medical industry: Production of syringes, test tubes, medical instruments, and other critical medical supplies.
- Packaging industry: Manufacturing of paper boxes, bottles, plastic bags, and diverse packaging solutions.
- Construction industry: Production of bricks, concrete pipes, decorative elements, and various construction components.
- Home appliance industry: Manufacturing of pots, pans, cutlery, kitchen utensils, and an array of household appliances.
3.2. Benefits of mold making
- Enhanced production efficiency: Molds automate manufacturing processes, significantly increasing production speed and minimizing labor costs.
- Superior product quality: Precision molds ensure consistent product dimensions, shapes, and features, delivering exceptional quality and uniformity.
- Cost reduction: Large-scale production using molds leads to substantial cost savings per unit, making products more affordable for consumers.
- Product diversification: Molds empower businesses to effortlessly introduce new products with intricate designs and complex shapes, expanding their product offerings.
- Increased competitive edge: Companies that utilize mold manufacturing services gain a competitive advantage through high-quality products, cost-effectiveness, and rapid production cycles.
Molds stand as testaments to human ingenuity and technological prowess, silently shaping the world around us. Their applications span across industries, transforming raw materials into products that enrich our lives and fuel economic growth. As technology advances and demand for innovative products intensifies, the role of mold manufacturing is poised to expand even further, shaping the future of manufacturing and defining the products that will define our world.
4. Contact us
Contact us today for a free consultation and quote
Email: ads.athardcoating@gmail.com
Mobile/Zalo: 0906 735 520
Hotline: 1900 9232


